1.1 Number Systems
As you have learnt about the number line and how to represent various types of numbers like — natural number, integers, fraction, decimal and so many.
Number system includes all the number types like - natural number, integers, fraction, decimal and so many. Continue Learning
2.1 Introduction
Well studied algebraic expressions, their addition, subtraction, multiplication and division in earlier classes.
(x + y)2 = x2 + 2xy + y2
(x — y)2 = x2 —2xy + y2
Here we start with a particular type of algebraic expression, called polynomial, and there terminology. Continue Learning
3.1 Introduction
The idea has far reaching consequences, and has given rise to a very important branch of Mathematics known as Coordinate Geometry.
The coordinate geometry or Cartesian geometry, using a coordinate system.
3.2 Cartesian System
The point from which the distances are marked is called the origin. Continue Learning
4.1 Introduction
We have studied linear equations in one variable. Here we learn more knowledge of linear equations in one variable shall be recalled and extended to that of two variables
4.2 Linear Equations
Consider the following equation: 2x + 5 = 0 in number line. Continue Learning
5.1 Introduction
The word ‘geometry’ comes form the Greek words ‘geo’, meaning the ‘earth’, and ‘metrein’, meaning ‘to measure’. Geometry appears to have originated from the need for measuring land. This branch of mathematics was studied in various forms in every ancient civilisation, be it in Egypt, Babylonia, China, India, Greece, the Incas, etc. The people of these civilisations faced several practical problems which required the development of geometry in various ways. Continue Learning
We have leant that we need a minimum of two points are required to draw a line.
Here we will study about the properties of the angles formed when two lines intersect each other, and also the properties of the angles formed when a line intersects two or more parallel lines at distinct points.
6.2 Basic Terms and Definitions
7.1 Introduction
As we learnt in previous class that, when three line intersecting each other and make a closed figure that's called Triangle.
Tri’ means ‘three’. A triangle has three sides, three angles and three vertices. For example, in triangle ABC, denoted as D ABC
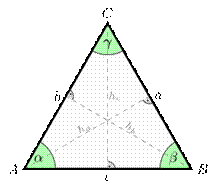
As we have learnt that a quadrilateral is a polygon with four edges and four vertices or corners.
As we learnt the joining three non–collinear points in pairs, the figure so obtained is a triangle, similarly we mark four points and see what we obtain on joining.
8.2 Angle Sum Property of a Quadrilateral
The sum of the angles of a quadrilateral is 360°. Continue Learning
9.1 Introduction
We are very familiar with the concept of the Triangles and congruent figures. Congruent means when two figures are called congruent, if they have the same shape and the same size.
The part of the plane enclosed by a simple closed figure is called a planar region corresponding to that figure. The magnitude or measure of this planar region is called its area. Continue Learning
10.1 Introduction
Circle which has round in shape, such as wheels of a vehicle, bangles, dials of many clocks, coins of denominations.
In simple way we can say that anything abound us having the round in shape is called Circle. Circles have radius and diameter and one center. Continue Learning
11.1 Introduction
We have learnt about the many shapes and diagrams, which were necessary to prove a theorem or solving exercises.
Normally, all these instruments are needed in drawing a geometrical figure, such as a triangle, a circle, a quadrilateral, a polygon, etc. with given measurements. But a geometrical construction is the process of drawing a geometrical figure using only two instruments — an ungraduated ruler, also called a straight edge and a compass. In construction where measurements are also required, you may use a graduated scale and protractor also. Continue Learning
12.1 Introduction
As we have learnt in earlier classes about figures of different shapes such as squares, rectangles, triangles and quadrilaterals. Also calculated perimeters and the areas of some of these figures like rectangle, square etc.
Unit of measurement for length or breadth is taken as metre (m) or centimeter (cm) etc. Continue Learning
13.1 Introduction
We have been dealing with figures that can be easily drawn on our notebooks or blackboards. These are called plane figures.
We have also understood what rectangles, squares and circles are, what we mean by their perimeters and areas, and how we can find them.
We shall now learn here to find the surface areas and volumes of cuboids and cylinders and so many. Continue Learning
14.1 Introduction
The word ‘statistics’ appears to have been derived from the Latin word ‘status’ meaning ‘a (political) state’. In its origin, statistics was simply the collection of data on different aspects of the life of people, useful to the share and show the information.
14.2 Collection of Data
Collection of data can be anything, when the information was collected by the investigator herself or Continue Learning
15.1 Introduction
We have learnt about the probability in previous classes. Here we will learn more, the words ‘probably’, ‘doubt’, ‘most probably’, ‘chances’, etc., used in the statements above involve an element of uncertainty.
It is remarkable that a science, which began with the consideration of games of chance, should be elevated to the rank of the most important subject of human knowledge. — Pierre Simon Laplace Continue Learning