1.1 Introduction
As we know about the Numbers e.g. 1, 2, 3, 4…. And so on. With the help of numbers we can easily counting the things is easy for us now.
While use of numbers we can know many things about them. Numbers help us Count concrete objects. It can be used in many different contexts and in many ways.
We enjoyed working with numbers in our previous classes. We have added, Subtracted, multiplied and divided them Now we Learn here some more. Continue Learning
2.1 Introduction
Whole Numbers the natural numbers along with zero form the collection is known as whole numbers.
For Example-: 0, 20, 42, 100 etc. not 4.2, 1 / 2 etc. Continue Learning
2.2 Whole Numbers
Whole Numbers
The natural numbers along with zero form the collection is known as whole numbers.
For Example-: 0, 20, 42, 100 etc. not 4.2, 1 / 4 etc.
3.1 Introduction
Now we are able to Playing with numbers. You can make addition, subtractions, Multiplications and divisions with the Numbers.
3.2 Factors and Multiples
Any number you multiply to get another number. The result that you get known as factor. Factor of a number is an exact divisor of that number.
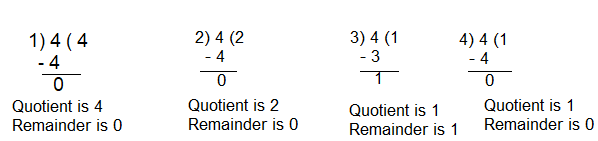 Continue Learning
Continue Learning
4.1 Introduction
Basic Geometrical Ideas
The term ‘Geometry’ is the English equivalent of the Greek word‘Geometron’.‘Geo’ means Earth and‘metron’ means Measurement. According to historians, the geometrical ideas shaped up in ancient times, probably due to the need in art, architecture and measurement.
4.2 Points
A Sharper the tip will be the dot. This dot is almost invisible, tiny dot can be said an idea of a point. A point determines a location. Continue Learning
5.1 Introduction
Elementary means fundamental, basic, primary. So, here we go to learn about these basic Shapes e.g. Triangles, Angles, Square, lines, Curves etc. We can learn about different shapes, there properties, measurements etc.
5.2 Measuring Line Segments
As we know that the distance between two or more point called line segments.
Here we can measure the distance of different line segments like−Triangles, Quadrilaterals of line segments.
Measure of each line segment is a unique number called its “length”. Continue Learning
6.1 Introduction
A counting number, zero, or the negative of a counting number. No fractions or decimals.
When you see on Number line before Zero (0) and after 0, use a sign going for numbers less than zero and greater that zero.
The sign that use is the placement of a minus sign before the zero numbers.
This indicates that numbers with a negative sign are less than zero. These are called negative numbers.
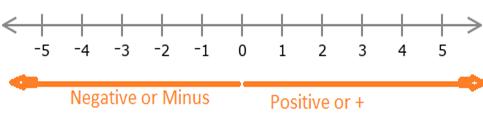
Tag me with a sign
We have seen yet some numbers carry a minus sign that's before zero or left hand side and some of are positive that's after zero or right hand side. Continue Learning
7.1 Introduction
Fraction is the word, the number system that you use in your daily life in many ways like- when you saying give me half glass of water, bite some pieces of bread etc, So fraction is the part of something and we can use it number system.
7.2 A Fraction
As we learn above Fraction tell us about how many parts of a anything that we have or see around. A fraction can be written with the slash that is written between the two numbers. In the fraction we have a top number called the numerator, and a bottom number called denominator. For example, 1/2 is a fraction. Continue Learning
8.1 Introduction
The decimal number system is the standard system for denoting integer and non-integer numbers. A number whose whole number part and the fractional part is separated by a decimal point.
8.2 Tenths
If we cut anything into the 10 pieces the 10th piece is known as tenth.
In fraction it’ll be represent 1/10 means something you divided into 10 equal parts of that unit.
In decimal we can represent this 0.10 or .10, 0 is denoting before the point/decimal because of .10 is not look well so, the better way is 0.10 similarly you can share the 6th of anything will be written 1/6 and in decimal 0.6 or 0.60 Continue Learning
9.1 Introduction
Data means a collection of numbers gathered to give some information that can help us to learn something more about that. Your daily attendance, exam-marks, game scores etc are the collection of same type of data that share some information.
9.2 Recording Data
Collection or counting of similar type of things are said to be recording some information, that can be count, arrange and share more about that thing. For example−Collection of pen or pencil you have and the information about them like how many similar colors in that, how many pen or pencil do you have etc. Continue Learning
10.1 Introduction
The term Menstruations coming from geometry, that concerned with measuring of lengths, areas and volumes etc of area.
It learn us to calculate the lengths, area, volumes and also comparing that.
10.2 Perimeter
Perimeter is the covered distance along with the boundary forming a that closed with such area of figure.
Perimeter of a rectangle
Perimeter of the rectangle = Sum of the lengths of its four sides. Continue Learning
11.1 Introduction
Algebra
When we calculate something using with some symbols to denote unknown or known numbers such method is known as Algebra.
Algebra is the sibling to geometry, analysis (calculus), number theory etc. this is a powerful tool for problem solving in science, engineering, economics, finance, architecture, ship-building and many other day-to-day.
In India many great Indian mathematicians, Aryabhatt (born 476AD), Brahmagupta (born 598AD), Mahavira (who lived around 850AD) and Bhaskara II (born 1114AD) and others, contributed a lot to the study of algebra. They gave names such as Beeja etc. So, in india this is called beejaganit. Continue Learning
12.1 Introduction
Ratio says how many times and proportion says equal to ratio.
12.2 Ratio
When we compared the two quantities in terms of ‘how many times’. This comparison is known as the Ratio. We denote ratio using symbol‘:’
3/1 says 3:1
Two quantities can be compared only if they are in the same unit. Continue Learning
13.1 Introduction
Symmetry is quite a common term used in day to day life. When we see certain figures with evenly balanced proportions, we say, “They are symmetrical”.
13.2 Making Symmetric Figures : Ink-blot Devils
Take a piece of paper. Fold it in half. Spill a few drops of ink on one half side. Now press the halves together.
13.3 Figures With Two Lines of Symmetry
One of the two set-squares in your instrument box has angles of measure 30°, 60°, 90°. Continue Learning
14.1 Introduction
Practical Geometry
14.2 The Circle
Every point on its boundary is at an equal distance from its centre.
14.3 A Line Segment
Line segment of length 4.7 cm.

With the help of compasses pointer Continue Learning