Basic Geometrical Ideas
The term ‘Geometry’ is the English equivalent of the Greek word‘Geometron’.‘Geo’ means Earth and‘metron’ means Measurement. According to historians, the geometrical ideas shaped up in ancient times, probably due to the need in art, architecture and measurement.
A Sharper the tip will be the dot. This dot is almost invisible, tiny dot can be said an idea of a point. A point determines a location.
Joint two or more Point or dot each will be a Line segment.
While any line segment from point A to point B (i.e. AB ) is extended beyond A in one direction and beyond B in the other direction without any end know as a line.

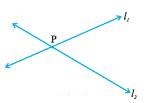
If two lines have crossed each other at some common point, they are called intersecting lines.
When two Line Segments going or standing opposite to each other, which do not meet are said to be parallel; and are called parallel lines.
A ray is a portion of a line. Those starts with a point (called starting point or initial point) and goes endlessly another Point same in a direction.
A curve is look like different shapes of Moon, not full moon and also like more or less similar.
If a curve does not cross itself, then it is called a simple curve.
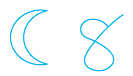
While a line or curve point has not connected each other is known as open curve.
While a line or curve point has connected each other at any point is known as closed curve.
The interior of a curve together with its boundary is called its “region”.
While two or more line segment connect to each other at any point are also simple closed curves. They are called polygons.
So, a figure is a polygon if it is a simple closed figure made up entirely of line segments. Draw ten differently shaped polygons.

The meeting point of a pair of sides is called its vertex.
Any two sides with a common end point are called the adjacent sides of the polygon.
The end points of the same side of a polygon are called the adjacent vertices.
When two or more line segments has connected at any point that make any corner, when the corners are formed that formed corner in known as Angle.
An angle is made up of two rays starting from a common initial point.
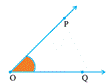
The two rays forming the angle are called the arms or sides of the angle.
The common initial point is the vertex of the angle.
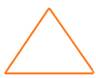
As name says tri angle, means A shape that formed with three angle. A triangle is a three-sided polygon. In fact, it is the polygon with the least number of sides.
A four sided polygon is a quadrilateral. It has 4 sides and 4 angles. As in the case of a triangle, you can visualise its interior too.
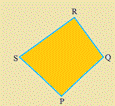
Note the cyclic manner in which the vertices are named.
Anything that we founded in rounded in shape is called Circle.
A circle is a simple closed curve which is not a polygon. It has some very special properties.
Naturally every point on the circle is at equal distance from the centre.

From equal distance from the centre is known as Radius.

Double of the radius is known as diameter.

chord connecting two points on a circle.
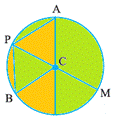
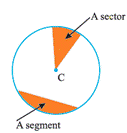
A region in the interior of a circle enclosed by an arc on one side and a pair of radii on the other two sides is called a sector.
A region in the interior of a circle enclosed by a chord and an arc is called a segment of the circle.
The distance around a circle is its circumference.
A diameter of a circle divides it into two equal parts; each part is a semi-circle. A semi-circle is half of a circle, with the end points of diameter as part of the boundary.