As we learnt about the Geometry, that's tell us about the different type of shapes, about their properties, measurements, volumes etc.
Here we learn more about the quadrilaterals having different shapes, sizes, measurements etc.
In this section we shall learn how to construct a unique quadrilateral given the following
Measurements:
When four sides and one diagonal are given.
When two diagonals and three sides are given.
When two adjacent sides and three angles are given.
When three sides and two included angles are given.
When other special properties are known.
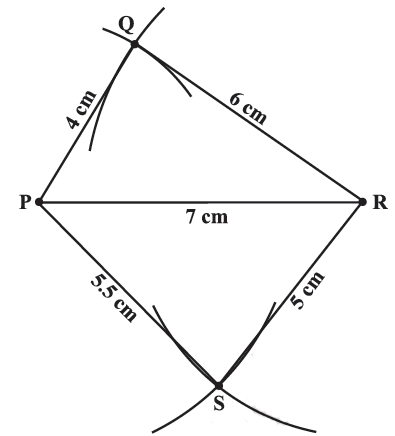
When the lengths of four sides and a diagonal are given
Construct a quadrilateral PQRS where PQ = 4 cm, QR = 6 cm, RS = 5 cm, PS = 5.5 cm and PR = 7 cm.
When two diagonals and three sides are given
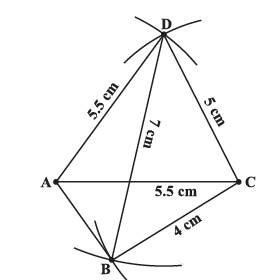
When four sides and a diagonal were given, we first drew a triangle with the available data and then tried to locate the fourth point.
For Example-: Construct a quadrilateral ABCD, given that BC = 4.5 cm, AD = 5.5 cm, CD = 5 cm the diagonal AC = 5.5 cm and diagonal BD = 7 cm.
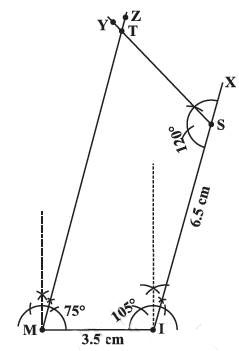
When two adjacent sides and three angles are known
Construct a quadrilateral MIST where MI = 3.5 cm, IS = 6.5 cm, ∠M = 75°, ∠I = 105° and ∠S = 120°.
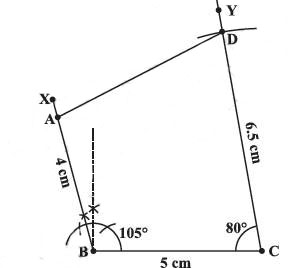
When three sides and two included angles are given
Construct a quadrilateral ABCD, where AB = 4 cm, BC = 5 cm, CD = 6.5 cm and ∠B = 105° and ∠C = 80°.
Some Special Cases
Some special cases means that saying about the different quadrilaterals having different shapes and sizes.
