Geometry teaching us about the area, perimeter, volumes etc of shapes. We had learnt in previous classes of many shapes.
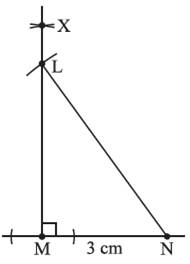
Here go to learn about the Constructions of Parallel Line with the help of point by using of ruler (scale that using of measurement available in your instrument box.) and compasses.
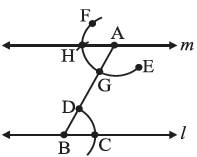
Here ∠ABC and ∠BAH are alternate interior angles. Therefore m || l
We learnt something more about the triangle. Triangles are classified based on sides or angles and the following important properties concerning triangles:
The exterior angle of a triangle is equal in measure to the sum of interior opposite angles.
The total measure of the three angles of a triangle is 180°.
Sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the length of the third side.
In any right-angled triangle, the square of the length of hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides.
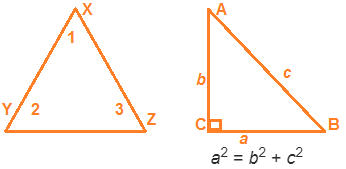
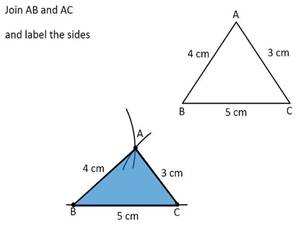
Here we would construct triangles when all its sides are known. The SSS known as Side-Side-Side, means there has three sides of triangle. Given the three side lengths of a triangle.
Draw a triangle with length of 3, 4 and 5 cm.
Here we have only two sides given and the one angle between them and then we have draw the triangle. The SAS creation means Side-Angle-Side, means has two sides and one Angle. Given the lengths of any two sides and the measure of the angle between these sides.
Draw a triangle with length of 4 and 5 cm.
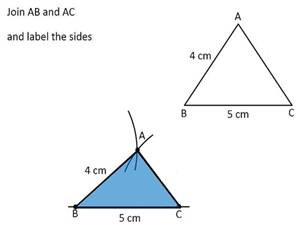
Here we have only two Angles given and the one Side between them and then we have draw the triangle. The ASA creation means Angle-Side-Angle, means has two angles and one side. Given the measures of two angles and the length of side included between them.
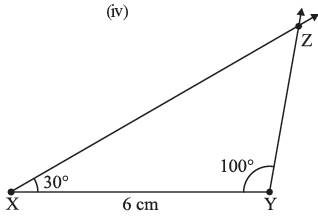
Construct △XYZ if it is given that XY = 6 cm, m∠ZXY = 30° and m∠XYZ = 100°.
Given the length of hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle and the length of one of its legs is known as RHS.