There are so many movements happen in our bodies. We can observe the movements taking place in our body.
There are so many movements that happen in our bodies.
Walk, run, fly, jump, creep, crawl, slither and swim − these are only a few of the ways in which animals move from one place to another.
Bend your arm at the elbow and the leg at the knee. Stretch your arm sideways. Bend your arm to touch your shoulder with your fingers. These all are the movements of the body parts.
When we are able to bend or rotate our body in places where two parts of our body seem to be joined together − like elbow, shoulder or neck these all places are known as joints.
While we press our fingers against the top of your head, face, neck, nose, ear, back of the shoulder, hands and legs including the fingers and toes. The hard structures are known as the bones.
There are different types of joints in our body to help us carry out different movements and activities.
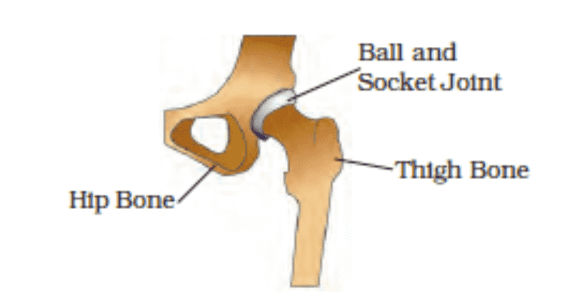
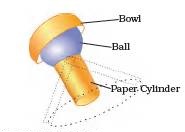
The bowl is like the part of the shoulder to which your arm is joined. The rounded end of one bone fits into the cavity (hollow space) of the other bone such joint allows movements in all directions.
Ball and socket joints
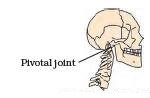
Pivotal Joint
The joint where our neck joins the head is a pivotal joint. It allows us to bend our head forward and backward and turn the head to our right or left.
Hinge joints - Open and close a door a few times. Observe the hinges of the door carefully.
Fixed joints - The bones cannot move at these joints. Such joints are called fixed joints.
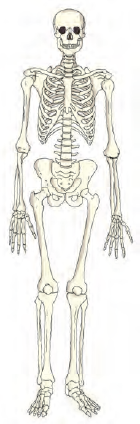
The human skeleton is composed of around 305 bones at birth. The number of bones in the skeleton changes with age. It decreases to 206 bones by adulthood after some bones have fused together. This framework is called the skeleton.
Sometimes when we are hurt or have an accident, the doctors use these X-ray images to find out about any possible injuries that might have happened to the bones. The X-rays show the shapes of the bones in our bodies.
There are many bones, isn’t flexible like write that's called carpals.
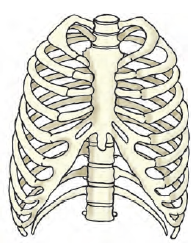
The bones join the chest bone and the backbone together to form a box. This is called the rib cage. There are 12 ribs on each side of chest. Some important internal parts of our body lie protected inside this cage.
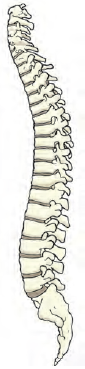
The backbone is made up of many small bones called vertebrae. The backbone consists of 33 vertebrae. The rib cage is joined to these bones.
The two bones on the back are prominent where are called shoulder bones.
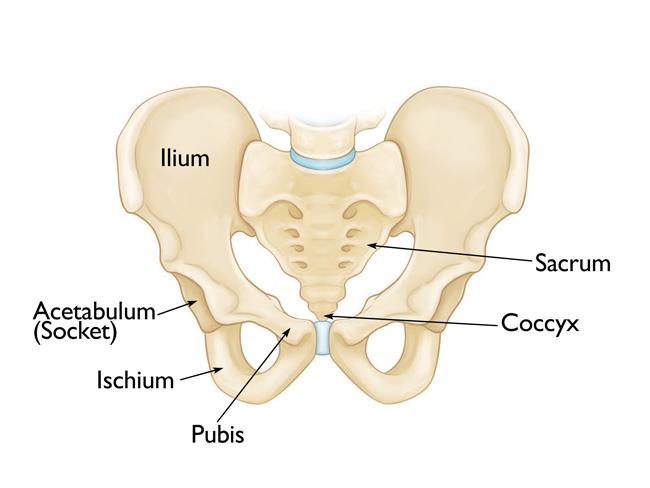
The Pelvic bones enclose the portion of your body below the stomach. This is the part when we sit on.
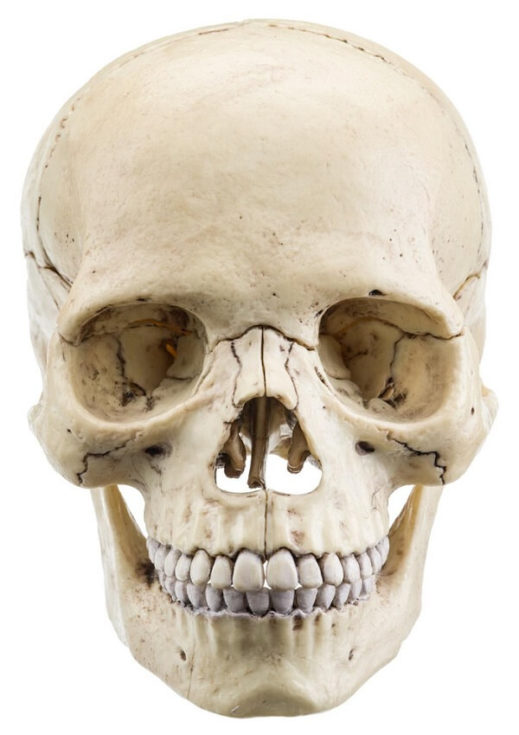
The skull is made up of many bones joined together It encloses and protects a very important part of the body, the brain.
We discussed many bones and the joints of our skeleton. There are some additional parts of the skeleton that are not as hard as the bones and which can be bent. These are called cartilage.
A swollen region is the upper arm is a muscle. The muscle bulged due to contraction. When contracted, the muscle becomes shorter, stiffer and thicker. It pulls the bone.
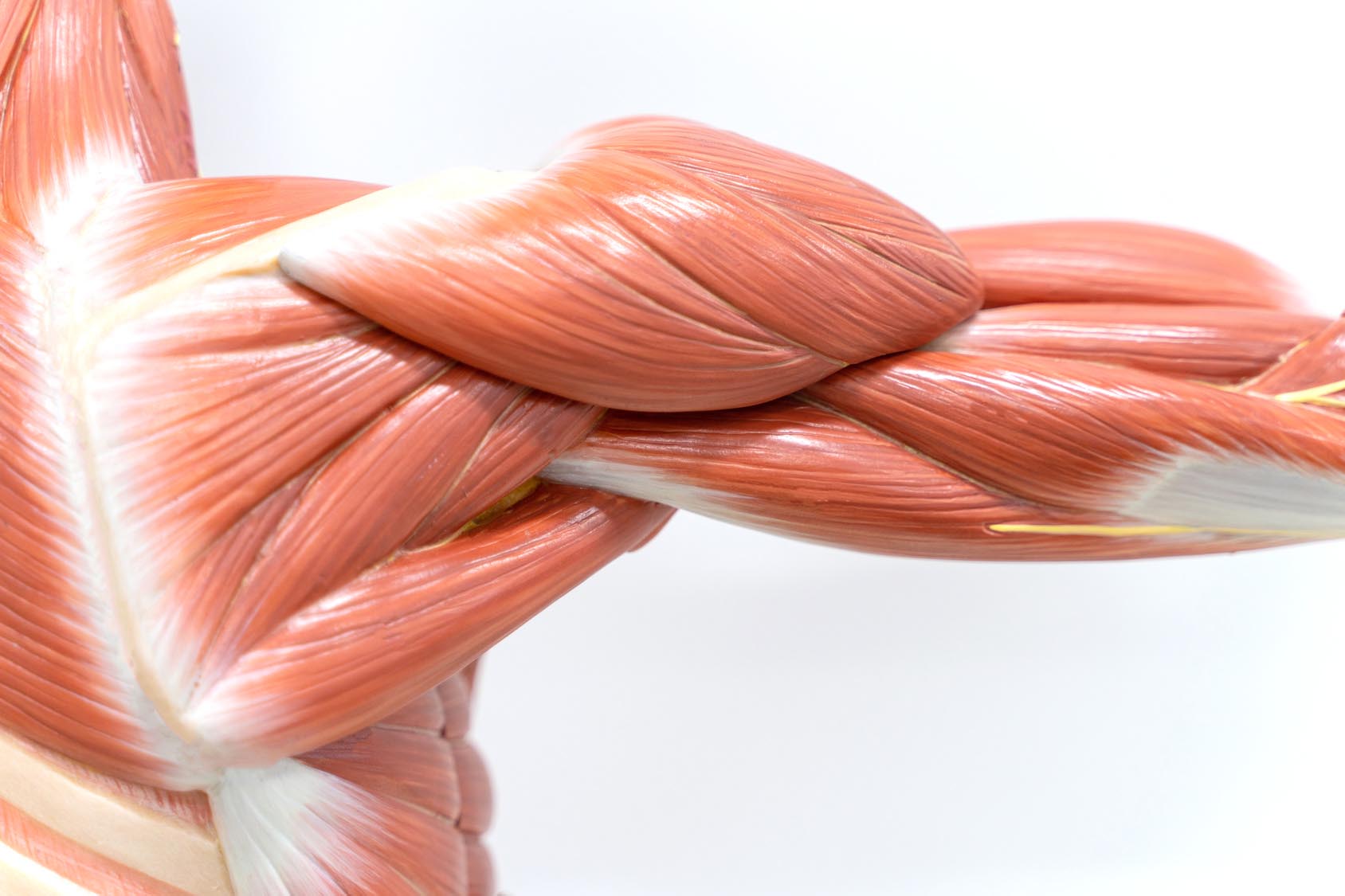

Muscles work in pairs. When one of them contracts, the bone is pulled in that direction. The other muscle of the pair relaxes. To move the bone in the opposite direction, the relaxed muscle contracts to pull the bone towards its original position, while the first relaxes.
A muscle can only pull. It cannot push. Thus, two muscles have to work together to move a bone.
Earthworm
An earthworm moving on soil in a garden in the farming fields. Gently lift it and place it on a piece of blotting or filter paper.
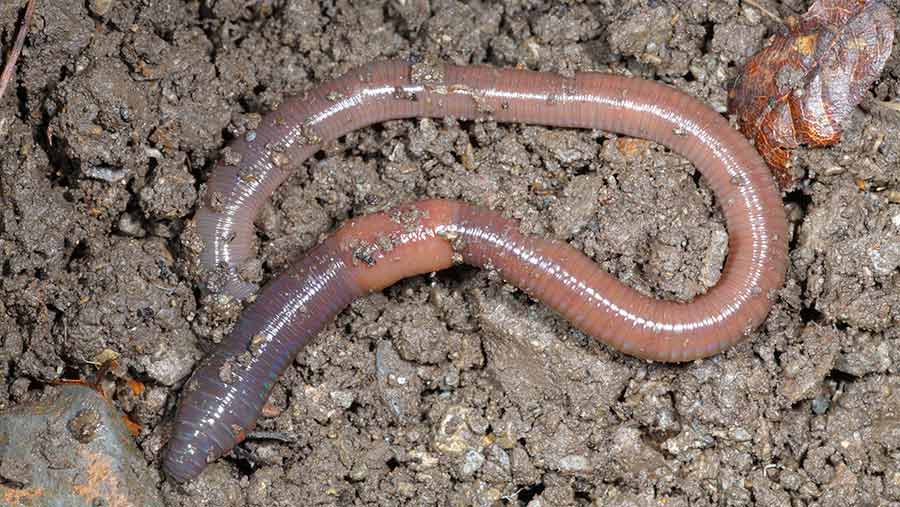

The body of an earthworm is made up of many rings joined end to end. An earthworm does not have bones. It has muscles which help to extend and shorten the body. During movement, the earthworm first extends the front part of the body, keeping the rear portion fixed to the ground. Then it fixes the front end and releases the rear end.
The earthworm, actually, eats its way through the soil! Its body then throws away the undigested part of the material that it eats.
Snail
A snail is also found in our garden or in field.
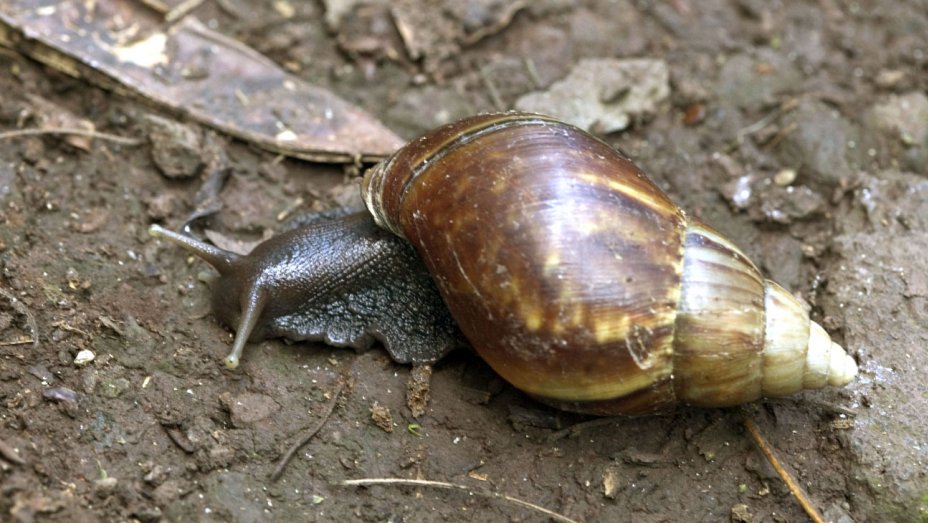

The shell and it is the outer skeleton of the snail, but is not made of bones. The shell is a single unit and does not help in moving from place to place.
Cockroach
Cockroaches walk and climb as well as fly in the air. They have three pairs of legs. These help in walking. The body is covered with a hard outer skeleton. This outer skeleton is made of number of plates joined together and that permits movement.
There are two pairs of wings attached to the body behind head. The cockroaches have distinct muscles − those near the legs move the legs for walking. The body muscles move the wings when the cockroach flies.

Birds
Birds fly in the air and walk on the ground. Some birds like ducks and swans also swim in water. The birds can fly because their bodies are well suited for flying. Their bones are hollow and light. The bones of the hind limbs are typical for walking and perching.
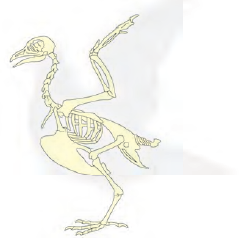
Fish
The head and tail of the fish are smaller than the middle portion of the body − the body tapers at both ends. These shape is called streamlined.
Fish also have other fins on their body which mainly help to keep the balance of the body and to keep direction, while swimming.
The shape is such that water can flow around it easily and allow the fish to move in water. The skeleton of the fish is covered with strong muscles. During swimming, muscles make the front part of the body curve to one side and the tail part swings towards the opposite side.
How do snakes move?
Snakes have a long backbone. They have many thin muscles. They are connected to each other even though they are far from one another. Muscles also interconnect the backbone, ribs and skin.
The snake's body curves into many loops. Each loop of the snake gives it a forward push by pressing against the ground. Since its long body makes many loops and each loop gives it this push, the snake moves forward very fast and not in a straight-line.

