We have learnt and familiar with some of the solids like cuboids, cone, cylinder, and sphere and also learnt how to find their surface areas and volumes.
Here we will learn how to find surface areas and volumes of objects.
13.2 Surface Area of a Combination of Solids
We learnt how to find the surface area of such a solid. But some time difficult to find the area of some surfaces, in that case we have to break that in to partitions and then find there surface area or volumes.
We can break it down into smaller shapes, and we will get the solutions.
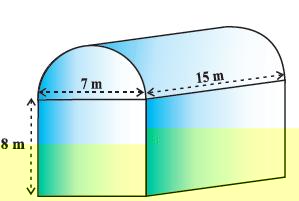
If we consider the surface of the newly formed object, we would be able to see only the curved surfaces of the two hemispheres and the curved surface of the cylinder.
So, the total surface area of the new solid is the sum of the curved surface areas of each of the individual parts.
The volume of the solid will be formed by joining two solids will actually the sum of the volumes of the constituents.
We learn here of one solid form change into another shape, for this scenario we have to take that if a candle in the shape of a solid cylinder, melt it and pour whole of the molten wax into another container shaped like a rabbit. On cooling, you will obtain a candle in the shape of the rabbit. The volume of the new candle will be the same as the volume of the earlier candle.
Here we can observed objects that are formed when two basic solids were joined together.
There will be in various formed.
