Reproduction is essential for the continuation of a species. Imagine what would have happened if organisms had not reproduced.
In plants, there are two modes by which animals reproduce. These are:
We have learnt in previously that the plants reproduce sexually have male and female reproductive parts.
Animals also, males and females have different reproductive parts or organs. Like plants, the reproductive parts in animals also produce gametes that fuse to form a zygote. It is the zygote which develops into a new individual.
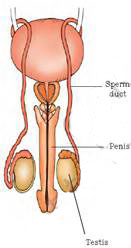
Male Reproductive Organs
The male reproductive organs include a pair of testes (singular, testis), two sperm ducts and a penis. The testes produce the male gametes called sperms. Millions of sperms are produced by the testes.
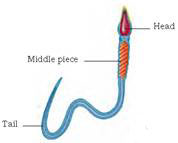
Sperms are very small in size, each has a head, a middle piece and a tail. sperm is a single cell with all the usual cell components.
Female Reproductive Organs
The female reproductive organs are a pair of ovaries, oviducts (fallopian tubes) and the uterus.
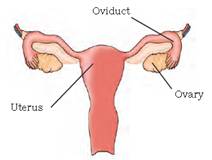
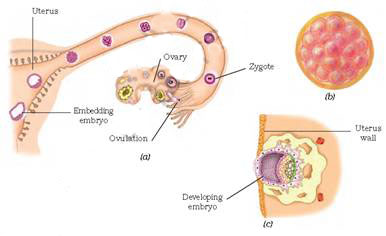
The ovary produces female gametes called ova (eggs). In human beings, a single matured egg is released into the oviduct by one of the ovaries every month. Uterus is the part where development of the baby takes place. Like the sperm, an egg is also a single cell.
Fertilisation
The first step in the process of reproduction is the fusion of a sperm and an ovum. When sperms come in contact with an egg, one of the sperms may fuse with the egg. Such fusion of the egg and the sperm is called fertilization.
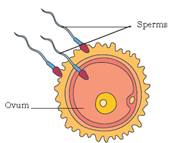
During fertilisation, the nuclei of the sperm and the egg fuse to form a single nucleus.
This results in the formation of a fertilised egg or zygote.
The process of fertilisation is the meeting of an egg cell from the mother and a sperm cell from the father. So, the new individual inherits some characteristics from the mother and some from the father.
Fertilisation which takes place inside the female body is called internal fertilisation. Internal fertilization occurs in many animals including humans, cows, dogs and hens.
When the sperms come in contact with the eggs. This results in fertilisation. This type of fertilisation in which the fusion of a male and a female gamete takes place outside the body of the female is called external fertilisation. It is very common in aquatic animals such as fish, starfish, etc.
Fertilisation which takes place inside the female body is called internal fertilisation. Internal fertilization occurs in many animals including humans, cows, dogs and hens.
Development of Embryo
Fertilisation results in the formation of zygote which begins to develop into an embryo. The zygote divides repeatedly to give rise to a ball of cells. The cells then begin to form groups that develop into different tissues and organs of the body. This developing structure is termed an embryo. The embryo gets embedded in the wall of the uterus for further development.
The embryo continues to develop in the uterus. It gradually develops body parts such as hands, legs, head, eyes, ears etc. The stage of the embryo in which all the body parts can be identified is called a foetus. When the development of the foetus is complete, the mother gives birth to the baby.
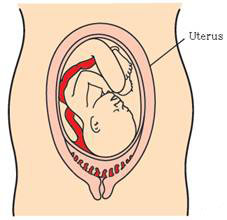
Viviparous and Oviparous Animals
The animals which give birth to young ones are called viviparous animals. Those animals which lay eggs are called oviparous animals.
Young Ones to Adults
The new individuals which are born or hatched from the eggs continue to grow till they become adults. In some animals, the young ones may look very different from the adults.
The transformation of the larva into an adult through drastic changes is called metamorphosis.
The bulges are the developing new individuals and they are called buds. In hydra too the new individuals develop as outgrowths from a single parent. This type of reproduction in which only a single parent is involved is called asexual reproduction. Since new individuals develop from the buds in hydra, this type of asexual reproduction is called budding.
Another method of asexual reproduction is observed in the microscopic organism, amoeba.
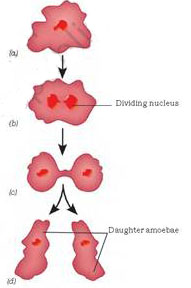
Asexual reproduction in which an animal reproduces by dividing into two individuals is called binary fission. Apart from budding and binary fission, there are other methods by which a single parent reproduces young ones.
