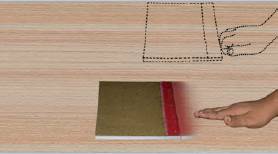
The force of friction always opposes the applied force. Like the force of friction acts between the surface of the book and the surface of the table.
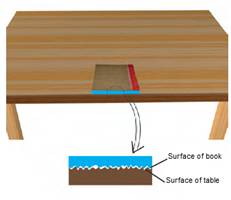
Friction is caused by the irregularities on the two surfaces in contact. Even those surfaces which appear very smooth have a large number of minute irregularities on them. Irregularities on the two surfaces lock into one another. When we attempt to move any surface, we have to apply a force to overcome interlocking.
On rough surfaces, there are a larger number of irregularities. So the force of friction is greater if a rough surface is involved.
The force required to overcome friction at the instant an object starts moving from rest is a measure of static friction. On the other hand, the force required to keep the object moving with the same speed is a measure of sliding friction.
If an object started moving, it would never stop if there were no friction. Had there been no friction between the tyres of the automobiles and the road, they could not be started or stopped or turned to change the direction of motion.
Friction is an evil, too. Friction can also produce heat. Vigorously rub your palms together for a few minutes. In fact, when a machine is operated, heat generated causes much wastage of energy.
We deliberately increase friction by using brake pads in the brake system of bicycles and automobiles.
Friction in order to increase efficiency. When oil, grease or graphite is applied between the moving part of a machine, a thin layer is formed there and moving surfaces do not directly rub against each other. Interlocking of irregularities is avoided to a great extent.
Movement becomes smooth. The substances which reduce friction are called lubricants.
In some machines, it may not be advisable to use oil as lubricant. An air cushion between the moving parts is used to reduce friction.
When one body rolls over the surface of another body, the resistance to its motion is called rolling friction. Rolling reduces friction. It is always easier to roll than to slide a body over another.
Since the rolling friction is smaller than the sliding friction, sliding is replaced in most machines by rolling by the use of ball bearings. Common examples are the use of ball bearings between hubs and the axles of ceiling fans and bicycles.
In science, the common name of gases and liquids is fluids. So we can say that fluids exert force of friction on objects in motion through them. The frictional force exerted by fluids is also called drag.
The frictional force on an object in a fluid depends on its speed with respect to the fluid. The frictional force also depends on the shape of the object and the nature of the fluid.
