When plants of the same kind are cultivated at one place on a large scale, it is called a crop.
If we talking about the India, then India is a vast country. The climatic conditions like temperature, humidity and rainfall vary from one region to another. Accordingly, there is a rich variety of crops grown in different parts of the country. Despite this diversity, two broad cropping patterns can be identified. There are:
Kharif Crops : The crops which are sown in the rainy season are called kharif crops. The rainy season in India is generally from June to September. Paddy, maize, soyabean, groundnut and cotton are kharif crops.
Rabi Crops : The crops grown in the winter season (October to March) are called rabi crops. Examples of rabi crops are wheat, gram, pea, mustard and linseed.
Cultivation of crops involves several activities undertaken by farmers over a period of time.
Agricultural practices which are listed below:
The preparation of soil is the first step before growing a crop. The process of loosening and turning of the soil is called tilling or ploughing.
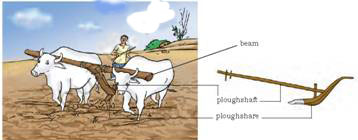
Plough : This is being used since ancient times for tilling the soil, adding fertilisers to the crop, removing the weeds and turning the soil.
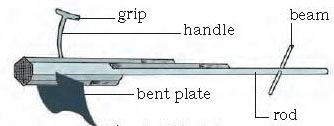
Hoe : It is a simple tool which is used for removing weeds and for loosening the soil. It has a long rod of wood or iron. A strong, broad and bent plate of iron is fixed to one of its ends and works like a blade.
Cultivator : Nowadays ploughing is done by tractor-driven cultivator. The use of cultivator saves labour and time.
Sowing is an important part of crop production. Before sowing, good quality, clean and healthy seeds of a good variety-are selected. Farmers prefer to use seeds which give high yield.
The substances which are added to the soil in the form of nutrients for the healthy growth of plants are called manure and fertilisers.
Soil supplies mineral nutrients to the crop plants. These nutrients are essential for the growth of plants. Continuous cultivation of crops makes the soil poor in nutrients.
Therefore, farmers have to add manure to the fields to replenish the soil with nutrients. This process is called manuring. Improper or insufficient manuring results in weak plants.
Manure is an organic substance obtained from the decomposition of plant or animal wastes. Farmers dump plant and animal waste in pits at open places and allow it to decompose. The decomposition is caused by some microorganisms.
Advantages of Manure : The organic manure is considered better than fertilisers. This is because-:
It enhances the water holding capacity of the soil.
It makes the soil porous due to which exchange of gases becomes easy.
It increases the number of friendly microbes.
It improves the texture of the soil.
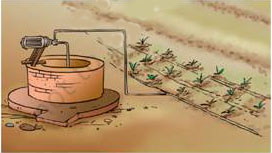
The supply of water to crops at regular intervals is called irrigation. Thevtime and frequency of irrigation varies from crop to crop, soil to soil and season to season.
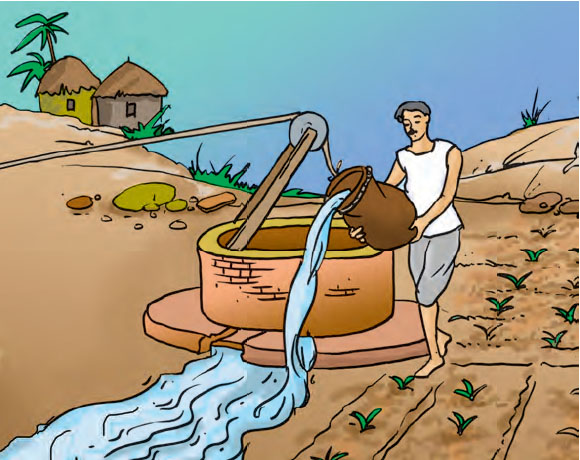
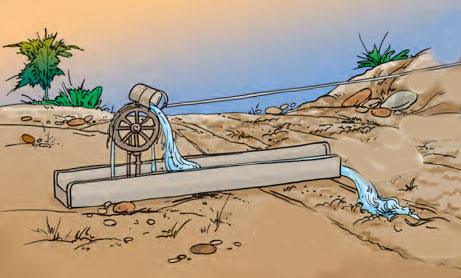
Sources of irrigation : The sources of water for irrigation are- wells, tubewells, ponds, lakes, rivers, dams and canals.
The various traditional ways are:



Modern Methods of Irrigation
Sprinkler System: This system is more useful on the uneven land where sufficient water is not available.
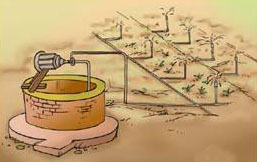
Drip system : In this system, the water falls drop by drop directly near the roots. So it is called drip system.
In a field many other undesirable plants may grow naturally along with the crop. These undesirable plants are called weeds.
The removal of weeds is called weeding. Weeding is necessary since weeds compete with the crop plants for water, nutrients, space and light.
The manual removal includes physical removal of weeds by uprooting or cutting them close to the ground, from time to time. This is done with the help of a khurpi. A seed drill is also used to uproot weeds.
Weeds are also controlled by using certain chemicals, called weedicides. These are sprayed in the fields to kill the weeds. They do not damage the crops. The weedicides are diluted with water to the extent required and sprayed in the fields with a sprayer.
Harvesting of a crop is an important task. The cutting of crop after it is mature is called harvesting.
In harvesting, crops are pulled out or cut close to the ground. It usually takes 3 to 4 months for a cereal crop to mature.

The harvested crop, the grain seeds need to be separated from the chaff. This process is called threshing. This is carried out with the help of a machine called ‘combine’ which is in fact a harvester as well as a thresher
Storage of produce is an important task. If the harvested grains are to be kept for longer time, they should be safe from moisture, insects, rats and microorganisms. Harvested grains have more moisture.
Farmers store grains in jute bags or metallic bins. However, large scale storage of grains is done in silos and granaries to protect them from pests like rats and insects
Dried neem leaves are used for storing food grains at home. For storing large quantities of grains in big godowns, specific chemical treatments are required to protect them from pests and microorganisms.
