A chemical process in which a substance reacts with oxygen to give off heat is called combustion. The substance that undergoes combustion is said to be combustible. It is also called a fuel. The fuel may be solid, liquid or gas. Sometimes, light is also given off during combustion, either as a flame or as a glow.
The lowest temperature at which a substance catches fire is called its ignition temperature.
The substances which have very low ignition temperature and can easily catch fire with a flame are called inflammable substances. Examples of inflammable substances are petrol, alcohol, Liquified Petroleum Gas (LPG) etc.
Water cools the combustible material so that its temperature is brought below its ignition temperature. It's prevents the fire from spreading. Water vapours also surround the combustible material, helping in cutting off the supply of air. So, the fire is extinguished.
The job of a fire extinguisher is to cut off the supply of air, or to bring down the temperature of the fuel, or both.
The type of combustion in which a material suddenly bursts into flames, without the application of any apparent cause is called spontaneous combustion.
A large amount of gas formed in the reaction is liberated. Such a reaction is called explosion.
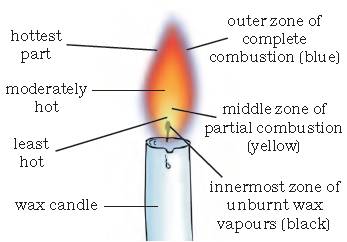
The substances which vapourise during burning, give flames. For example, kerosene oil and molten wax rise through the wick and are vapourised during burning and form flames. When the candle flame is steady, introduce a clean glass plate/slide into the luminous zone of the flame.
These substances are called fuels. A good fuel is one which is readily available.
There is probably no fuel that could be considered as an ideal fuel.
The sources of heat energy for domestic and industrial purposes are mainly wood, charcoal, petrol, kerosene etc. These substances are called fuels. A good fuel is one which is readily available.
The amount of heat energy produced on complete combustion of 1 kg of a fuel is called its calorific value. The calorific value of a fuel is expressed in a unit called kilojoule per kg (kJ/kg).
Combustion of most fuels releases carbon dioxide in the environment. Increased concentration of carbon dioxide in the air is believed to cause global warming.
Burning of coal and diesel releases sulphur dioxide gas. It is an extremely suffocating and corrosive gas. Moreover, petrol engines give off gaseous oxides of nitrogen. Oxides of sulphur and nitrogen dissolve in rain water and form acids. Such rain is called acid rain.
