The production of new individuals from their parents is known as reproduction.
There has the different mode of reproduction based on the category of organism. Plant has different mode of reproduction as compared with human, as different with animals etc.
In plant the flowers perform the function of reproduction in plants. Flowers are the reproductive parts.
There are several ways by which plants produce their offspring. These are categorised into two types: (i) asexual, and (ii) sexual reproduction.
In asexual reproduction plants can give rise to new plants without seeds, whereas in sexual reproduction, new plants are obtained from seeds.
Asexual reproduction- In asexual reproduction new plants are obtained without production of seeds.
Vegetative propagation- It is a type of asexual reproduction in which new plants are produced from roots, stems, leaves and buds
Budding- The small bulb-like projection coming out from the yeast cell is called a bud. The bud gradually grows and gets detached from the parent cell and forms a new yeast cell. The new yeast cell grows, matures and produces more yeast cells.
Fragmentation-water and nutrients are available algae grow and multiply rapidly by fragmentation. An alga breaks up into two or more fragments. These fragments or pieces grow into new individuals.
Spore formation- Spores are asexual reproductive bodies. Each spore is covered by a hard protective coat to withstand unfavourable conditions such as high temperature and low humidity. So they can survive for a long time.
We know that the flowers are the reproductive parts of a plant. Stamens are the male reproductive part and pistil is the female reproductive part.
Flowers which contain either only pistil or only stamens are called unisexual flowers. Flowers which contain both stamens and pistil are called bisexual flowers. Corn, papaya and cucumber produce unisexual flowers, whereas mustard, rose and petunia have bisexual flowers.
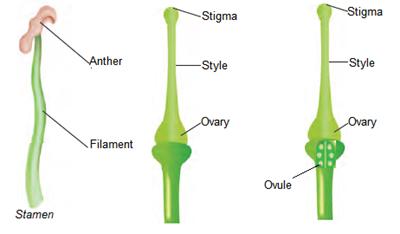
Stamens are the male reproductive part and pistil is the female reproductive part
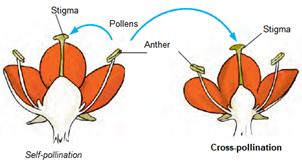
Pollination- The transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma of a flower is called pollination.
If the pollen lands on the stigma of the same flower or another flower of the same plant, it is called self-pollination. When the pollen of a flower lands on the stigma of a flower of a different plant of the same kind, it is called cross-pollination.
Fertilisation-The cell which results after fusion of the gametes is called a zygote. The process of fusion of male and female gametes (to form a zygote) is called fertilization. The zygote develops into an embryo.
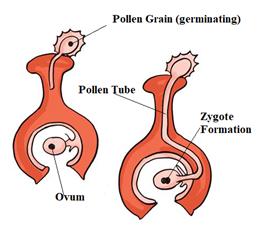
After fertilisation, the ovary grows into a fruit and other parts of the flower fall off. The fruit is the ripened ovary. The seeds develop from the ovules. The seed contains an embryo enclosed in a protective seed coat.
In the nature there are same kind of plants grow at different places. It's happens because seeds are dispersed to different places.
Seeds and fruits of plants are carried away by wind, water and animals. Winged seeds such as those of drumstick and maple.
Some seeds are dispersed by water. These fruits or seeds usually develop floating ability in the form of spongy or fibrous outer coat as in coconut. Some seeds are dispersed by animals, especially spiny seeds with hooks which get attached to the bodies of animals and are carried to distant places.
