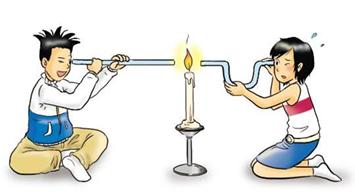
The candle, which appears behind the mirror, is the image of the candle formed by the mirror. The candle itself is the object.
When we see a mirror changes the direction of light that falls on it, the change of direction by a mirror is called reflection of light.
When we see in the mirror the ‘right’ appears ‘left’ and the ‘left’ appears ‘right’. Note that only sides are interchanged; the image does not appear upside down.
Similarly when the driver of a vehicle ahead of an ambulance looks in her/his rear view mirror, she/he can read ‘AMBULANCE’ written on it and give way to it. It is the duty of every one of us to allow an ambulance to pass without blocking its way.
An image formed on a screen is called a real image.
If you increase the distance of the spoon from your face, you may see your image inverted. The curved shining surface of a spoon acts as a mirror. The most common example of a curved mirror is a spherical mirror.
If the reflecting surface of a spherical mirror is concave, it is called a concave mirror. If the reflecting surface is convex, then it is a convex mirror.
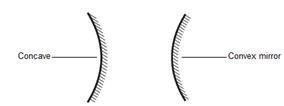
The inner surface of a spoon acts like a concave mirror, while its outer surface acts like a convex mirror.
An image formed on a screen is called a real image and the image formed by a plane mirror could not be obtained on a screen. Such an image is called a virtual image.
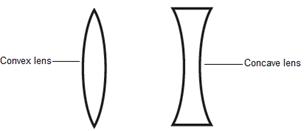
We have seen a magnifying glass. It's actually a type of a lens. Lenses are widely used in spectacles, telescopes and microscopes.
The lenses which feel thicker in the middle than at the edges are convex lenses and the lenses which feel thinner in the middle than at the edges are concave lenses.
The white light consists of seven colours.
